Shaft alignment, flatness, straightness, alignment measurements.
Measurement of straightness
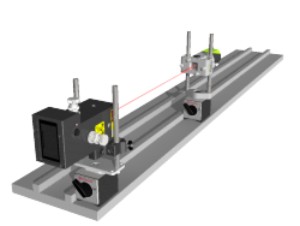
Straightness is measured in two axes, with the laser beam being used as a reference. The distance between the laser beam and the measured object is measured using a receiver in two or more positions.
Alignment of vertical and horizontal shafts.
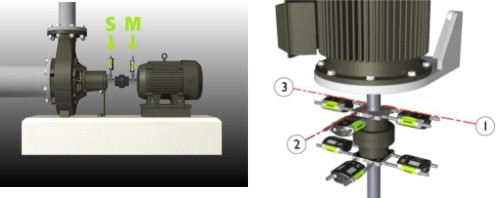
Shaft alignment means the alignment of two or more coupled machines so that the axes of the shafts are on a straight line. The alignment is performed in the horizontal and vertical directions - in the horizontal direction by sliding the machine on, in the vertical direction by inserting or removing washers from below the machine feet.
Measurement of Cardan Shaft Parallelism.

Cardan shafts are used to compensate for parallel misalignment (vertical / horizontal) between the driving and driven shafts. However, they cannot absorb angular misalignment between the shafts.
Angular misalignment typically results in increased vibrations, which may cause the driven shaft to rotate unevenly during operation.
DIAGO now allows fast and easy measuring of the parallelism of two shafts coupled by a cardan shaft on machines at standstill. Using our unique and patented technology, you no longer need to dismantle the cardan shaft.
Alignment of holes.

A clockwise method is used to measure the straightness of the holes. When measured by this method, the laser beam is set approximately parallel to the centerline. The center position of the hole is then measured so that the receiver records the measurements at two points, between which 180 °.
Two points serve as reference points.
Typical applications are hole measurements, e.g. bearing pins for compressors and diesel engines.
Alignment of pulleys
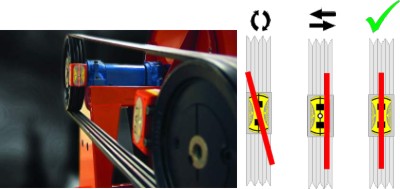
One of the common reasons for unplanned downtime of belt–driven machinery is pulley misalignment. Pulley misalignment can increase wear on pulleys and belts as well as increasing the noise and vibration levels, which can result in unplanned machinery downtime. Another side effect of increased vibration is premature bearing failure. This too can cause unplanned machinery downtime.
Accurate pulley and belt alignment can help you:
- Increase bearing life
- Increase machinery uptime, efficiency and productivity
- Reduce wear on pulleys and belts
- Reduce friction and thereby energy consumption
- Reduce noise and vibration
- Reduce costs of replacing components and machinery downtime
Flatness measurement
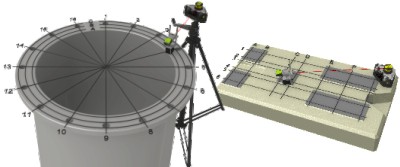
In the application of circular flatness, the laser plane is used as a reference. The deviation in the distance between the laser plane and the measured object is measured by the receiver in one or more positions.
Typical applications are flange measurements and circular machine foundations.
Measurement of rectangular flatness
In a rectangular planar application, a laser plane is used as a reference. The deviation in the distance between the laser plane and the measured object is measured by the receiver in one or more positions.
Typical applications are flatness measurements of machine beds and foundations.
It is particularly advantageous to combine flatness measurement with shaft alignment when installing the assembly.
